Supports Wake-on: pumbg Wake-on: g. Htpc# ethtool eth0. Supports Wake-on: g Wake-on: g. Each letter stands for a specific mode but in most cases the g mode (Magic Packet) should be ok. In my case my HTPC only supports g while my notebook supports the modes p, u, m, b and g. I only use the g mode. If youe need to change the WOL mode then. Supports Wake-on: pumbg Wake-on: g Current message level: 0x00000033 (51) Link detected: yes So it looks like to me that the router isn't advertising it's gigabit compatible.
This laptop has wake on lan enabled on bios side.
I checked also from shell
ethtool eth0 | grep -i wake
Supports Wake-on: pumbg
Wake-on: g
I turned off the laptop and tried to wake it from another linux server by
wakeonlan <macaddress>
etherwake <macaddress> -D
and also by an app from a windows 10 pc.
It doesn't turn on!
I looked the /etc/network/interfaces file and there are no option related to wake on lan.
So I wonder if the wake-on get disabled during boot by some instruction I don't know about.
thank you.

Introduction
The typical steps to make your Ubuntu server wake on LAN are:
- Find your network card interface name
- Check your network card capabilities
- Use ethtool to set “Wake-on” option to “g” value
And that’s all, then you put your server in suspend or hibernate mode and wake it up remotely. It works like a charm, but then you try a second time, you hibernate the server again and… it doesn’t wake remotely.
What happened, is that you didn’t repeat the third step to set again the “Wake-on” option to “g” value. The value you set for the network interface is volatile and you have to repeat the third step on each boot… unless you make it sticky.
Setup the network interface to work just once
Wake On Lan Debian
1.- Find your network card interface name
In my case, the server has three interfaces:
1: lo (the local loopback)
2: enp3s0: one 100Mbps ethernet card (not being used)
3: eno1: one 1Gbs ethernet card (this is the one I want to use to wake the system remotely, as it is the one configured to connect to my LAN). I will copy two values:
Interface name: eno1 (be aware of one (1) and lowercase L (l)). Usually interface name ends with a number, not a letter.
MAC address: e8:94:f6:08:5a:60
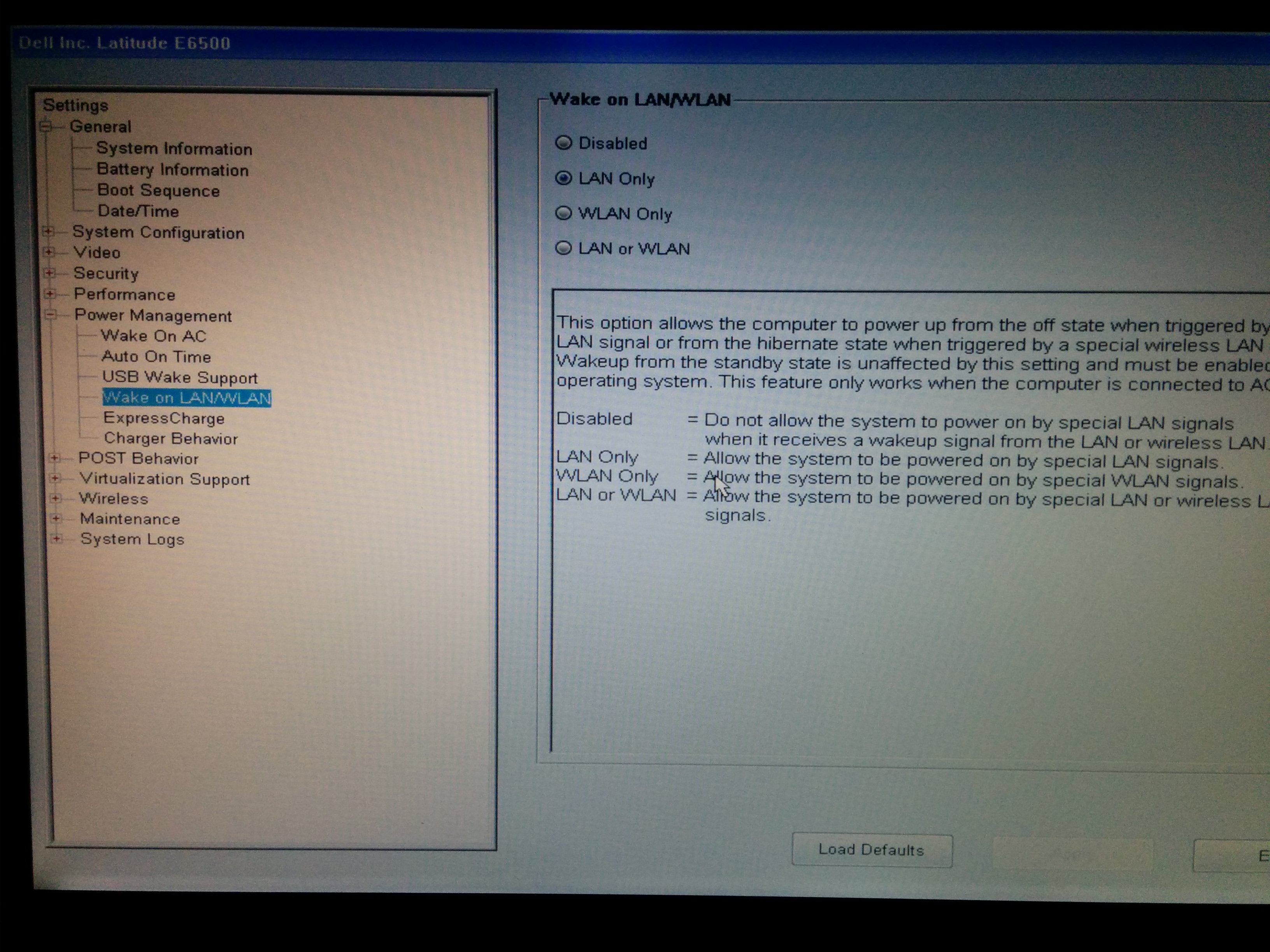
Now we know the interface name, we will check the Wake-on capabilities:
Take a look at the last lines. We are looking for two different lines:
Supports Wake-on: pumbg
and
Wake-on: d
The “Wake-on” mode configured by default is “d”, which means that the network card will not switch on the server when it receives a magic packet but, as the network interface supports “g” mode (it is one the letters in pumbg) we can set the value of “Wake-on” to “g”.
We will use ethtool for this. If it is not already installed on your system, do it:
Now, if you repeat the step to check your network card capabilities (ethtool eno1) you shoud see the “Wake-on” option set to “g” value.
That means your server is ready to sleep and wake remotely.
Put the server into hibernation mode:
And now wake it remotely using one of the many available tools. Depending on the platform you will use an Android, Windows, Linux, … tool for this purpose and the only thing you will need is the MAC address you copied some steps above.
Centos Wake On Lan
If everything went right, your server has woken, but what if you repeat the previous steps? (hibernate – remotely wake) It doesn’t work.
As I mentioned in the introduction, the value you configure in the “Wake-on” option of your network card is volatile. Each time you reboot your server it resets its value (usually to “d”).
Make your configuration sticky
We will create a system service to set the “Wake-on” value to “g” each time the server boots or restart.
There are a lot of recipes for these, but most of them didn’t work in my case. I’ll tell you one configuration line that did the trick for me.
1.- Create the .service file using your favourite editor
Now, copy the next content inside the file (change the name of the interface card and set the description you prefer):
Save the file (^O + ENTER + ^X)
Now we will start the service for the first time
And check its status
You will notice the service is dead or inactive. This is normal because it is not actually a service and it is not running like a daemon, it starts, do whatever it has to do and finishes.
If we restart the server now, our service entry will not run at startup because we haven’t enabled it. To do so:
Now, you can restart the server and it will wake remotely because “Wake-on: g” should be already set when it boots.
The explanation to “TRULY sticky”
But, why did I titled my post with a “TRULY sticky”?. Well, the reason is that all the recipes I’ve found to do this didn’t work. After rebooting, always the “d” value was set for the “Wake-on” option.
In fact it is not a problem of executing the configuration or not. Although the service entry run on every reboot, it was doing it before the network card was available to be configured.
So, the problem is when to run the network card configuration.
That’s the reason you should put this line in you .service file:
To make sure it configures the network card when it’s really available.
Proxmox Enable Wake On Lan
I hope it to work for you too.